
Key Takeaways
- Z-Image Base is the undistilled foundation model of the Z-Image family, optimized for fine-tuning and custom development rather than speed
- Supports CFG (Classifier-Free Guidance) and negative prompting for precise control, unlike the distilled Turbo variant
- Requires 28-50 inference steps vs Turbo’s 8 steps, trading speed for flexibility and higher diversity
- Uses 16GB VRAM minimum with 25GB optimal for 1024×1024 generation
- Built on Scalable Single-Stream DiT (S3-DiT) architecture with 6 billion parameters
- Community-ready for LoRA training, ControlNet integration, and industry-specific fine-tuning
Table of Contents
What is Z-Image Base?
Z-Image Base (officially called “Z-Image”) is the non-distilled foundation model underlying the Z-Image family of text-to-image generators. Released on January 27, 2026, it serves as the raw, versatile checkpoint designed specifically for developers, researchers, and creators who need maximum control and customization rather than pure speed.
Unlike Z-Image Turbo—which sacrifices flexibility for sub-second inference through distillation and reinforcement learning—Z-Image Base preserves the complete training signal. This makes it the ideal starting point for:
- Custom fine-tuning (LoRA, full training)
- Domain-specific adaptation (product photography, architectural visualization, brand aesthetics)
- Structural conditioning (ControlNet, depth maps, pose guidance)
- Research and experimentation requiring full CFG control
The Z-Image Model Family Hierarchy
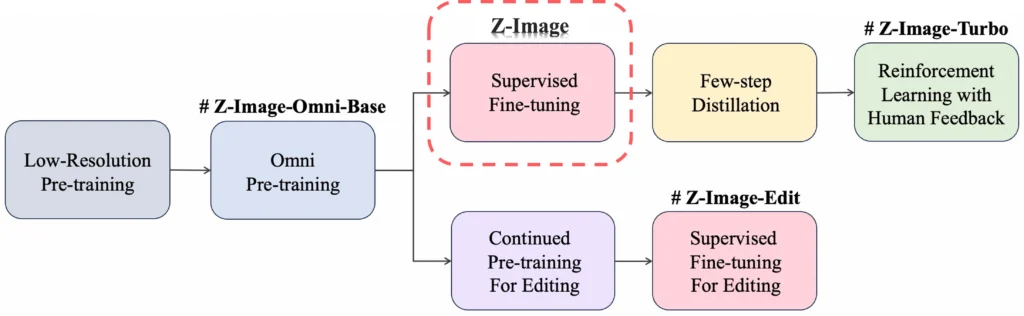
The Z-Image ecosystem consists of four specialized variants, each produced at different training stages:
| Model | Purpose | CFG Support | Steps | Fine-Tunable | Best For |
| Z-Image Base | Foundation | ✅ | 28-50 | ✅ | Development, fine-tuning |
| Z-Image Turbo | Speed | ❌ | 8 | ❌ | Production, real-time |
| Z-Image-Omni-Base | Multi-task | ✅ | 50 | ✅ | Gen + editing workflows |
| Z-Image-Edit | Editing | ✅ | 50 | ✅ | Image-to-image tasks |
Why Choose Z-Image Base Over Z-Image Turbo?
When Z-Image Base is the Right Choice
Choose Z-Image Base when you need development flexibility over production speed. The base model excels in scenarios requiring:
1. Fine-tuning and customization – Train LoRAs for specific visual styles, product categories, or brand identities
2. Negative prompt control – Suppress unwanted elements (artifacts, compositions, specific objects) with high fidelity
3. Output diversity – Generate varied compositions, facial identities, and lighting setups across different seeds
4. CFG-based prompt engineering – Leverage guidance scales (3.0-5.0) for complex professional workflows
5. Research and experimentation – Access the full undistilled model for academic or technical exploration
When Z-Image Turbo is the Right Choice
Choose Z-Image Turbo when you prioritize visual quality and inference speed. The distilled model is superior for:
- Production deployments requiring sub-second latency
- Photorealistic rendering with RL-enhanced aesthetics
- Bilingual text generation (English and Chinese character accuracy)
- Direct generation workflows without custom training needs
- Consumer hardware (runs efficiently on 16GB VRAM devices)
Performance Comparison
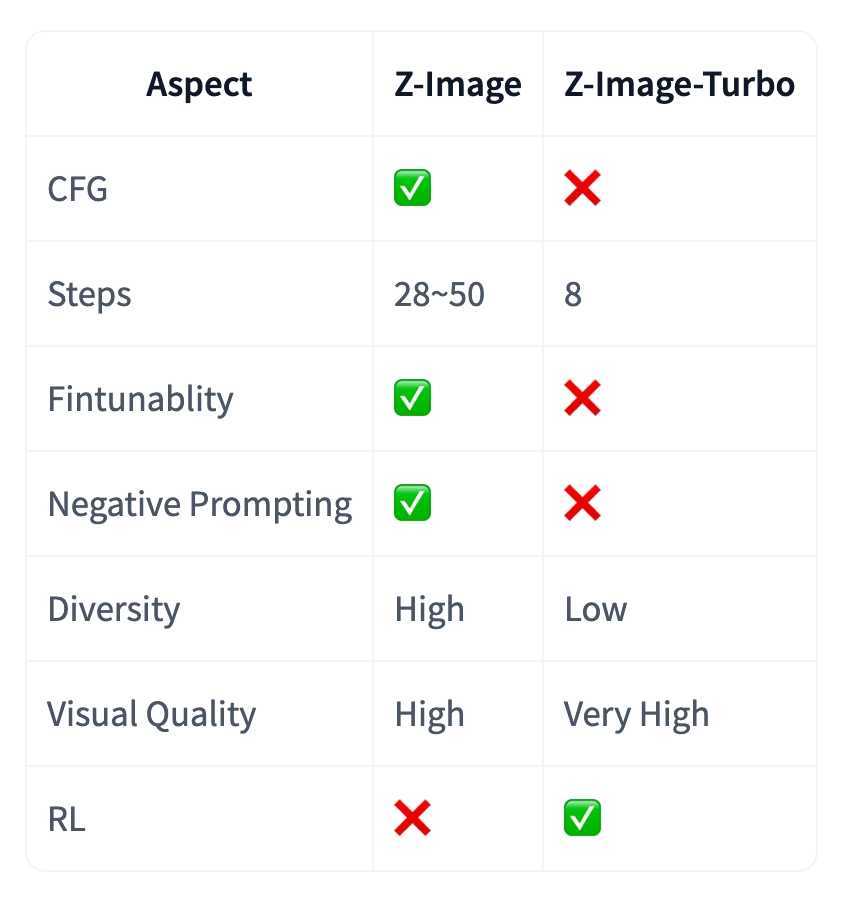
On RTX 4090 24GB hardware generating 1024×1024 images:
- Z-Image Base: 36 seconds (30 steps, CFG=4), 25GB VRAM
- Z-Image Turbo: 8 seconds (8 steps, no CFG), 16GB VRAM
The 4.5× speed difference reflects the fundamental trade-off: Base offers development potential, Turbo delivers production efficiency.
Z-Image Base Technical Specifications
Model Architecture
Z-Image Base employs a Scalable Single-Stream DiT (S3-DiT) architecture where text tokens, visual semantic tokens, and image VAE tokens are concatenated at the sequence level. This unified input stream maximizes parameter efficiency compared to dual-stream approaches.
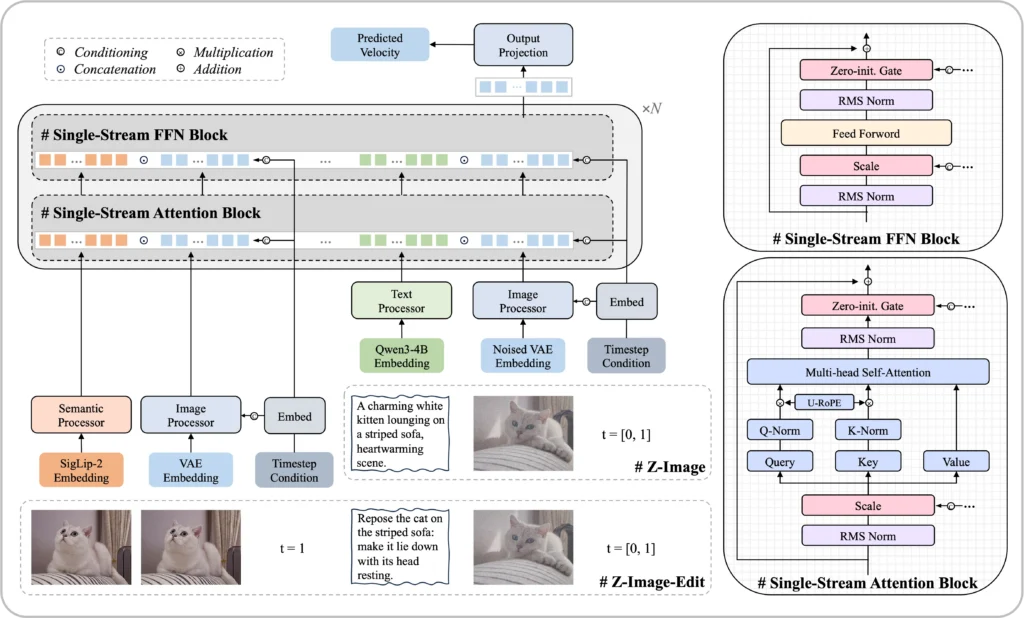
Core specifications:
- Parameters: 6 billion
- Training stages: Pre-training + Supervised Fine-Tuning (no RL)
- VAE: Uses FLUX.1 autoencoder (ae.safetensors)
- Text encoder: Qwen 3 4B model
- Precision: BFloat16 recommended for optimal performance
Recommended Generation Parameters
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Notes |
| Resolution | 512×512 to 2048×2048 | Any aspect ratio supported |
| Guidance Scale (CFG) | 3.0 – 5.0 | Higher = stronger prompt adherence |
| Inference Steps | 28 – 50 | 30-35 for balanced quality/speed |
| Negative Prompt | Strongly recommended | Essential for artifact suppression |
| CFG Normalization | False (default) | Set True for realism emphasis |
Z-Image Base Workflow Setup
Installation and Model Download
Step 1: Install Diffusers from source
Z-Image support requires the latest diffusers features:
| pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers |
Step 2: Download model files
For ComfyUI workflows, download these three components:
1. Text Encoder (Qwen 3 4B)
| Download: qwen_3_4b.safetensorsLocation: ComfyUI/models/text_encoders/ |
2. Diffusion Model (Z-Image Base)
| Download: z_image_bf16.safetensorsLocation: ComfyUI/models/diffusion_models/ |
3. VAE (FLUX.1 autoencoder)
| Download: ae.safetensors (rename to flux_ae.safetensors)Location: ComfyUI/models/vae/flux/ |
Step 3: Verify installation
| import torch from diffusers import ZImagePipeline pipe = ZImagePipeline.from_pretrained( “Tongyi-MAI/Z-Image”, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, low_cpu_mem_usage=False, ) pipe.to(“cuda”) |
Basic Generation Code
| prompt = “Young Asian woman in red Hanfu with intricate embroidery, impeccable makeup, elaborate high bun with golden phoenix headdress. Soft-lit outdoor night, silhouetted tiered pagoda background.” negative_prompt = “oversaturated, overexposed, static, blurry details, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, deformed hands, poorly drawn face” image = pipe( prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, height=1024, width=1024, cfg_normalization=False, num_inference_steps=35, guidance_scale=4.0, generator=torch.Generator(“cuda”).manual_seed(42), ).images[0] image.save(“output.png”) |
ComfyUI Official Workflow Parameters
The ComfyUI team recommends these settings for Z-Image Base:
- CFG Scale: 4-7 (higher values increase prompt adherence)
- Steps: 30-50 (diminishing returns after 40 steps for most prompts)
- Negative Prompt Template (tested across official workflows):
oversaturated colors, overexposure, static composition, blurred details, subtitles, stylized artwork, painting look, still image, overall gray cast, worst quality, low quality, jpeg compression artifacts, ugly, incomplete, extra fingers, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, deformed, disfigured, malformed limbs, fused fingers, static frozen pose, cluttered background, three legs, crowded background people, walking backward
Z-Image Base GGUF Support and Optimization
What is GGUF Format?
GGUF (GPT-Generated Unified Format) is a quantized model format that significantly reduces VRAM requirements while maintaining acceptable quality. For Z-Image Base, GGUF conversions enable:
- Lower VRAM usage (down to 4GB on compatible hardware)
- CPU offloading for memory-constrained devices
- Cross-platform deployment (CUDA, Vulkan, Metal)
Community GGUF Implementations
The stable-diffusion.cpp project provides pure C++ inference for Z-Image, allowing generation on GPUs with as little as 4GB VRAM. This is particularly valuable for:
- Consumer laptops with limited GPU memory
- Multi-model workflows where VRAM is shared
- Edge deployment scenarios
Installation example:
| # Clone stable-diffusion.cpp git clone https://github.com/leejet/stable-diffusion.cpp cd stable-diffusion.cpp # Build with CUDA support mkdir build && cd build cmake .. -DSD_CUBLAS=ON cmake –build . –config Release # Run Z-Image inference ./bin/sd -m z_image_base_q4_0.gguf -p “your prompt” –cfg-scale 4.0 –steps 35 |
Performance Trade-offs
| Format | VRAM | Speed | Quality Loss |
| BF16 (original) | 25GB | Baseline | 0% |
| FP16 | 20GB | ~5% faster | <1% |
| GGUF Q8 | 12GB | ~15% slower | ~2% |
| GGUF Q4 | 6GB | ~35% slower | ~5% |
Advanced Techniques for Z-Image Base
Structured Prompting with JSON
For complex, repeatable workflows, structure prompts as JSON objects before converting to text. This approach improves:
- Consistency across batch generations
- Modularity when adjusting specific elements
- Version control for prompt iterations
Example JSON structure:
| { “subject”: { “identity”: “young East Asian woman”, “hair”: “long black wavy hair”, “expression”: “subtle smile” }, “scene”: { “location”: “minimalist studio”, “background”: “clean neutral backdrop” }, “camera”: { “shot”: “half body”, “lens”: “85mm portrait lens” }, “lighting”: { “style”: “soft cinematic key light”, “detail”: “gentle rim light” }, “negative”: [“low quality”, “deformed hands”, “blurry face”] } |
Convert to prompt text using ComfyUI’s comfyui-jsonprompt node or custom Python scripts.
Fine-Tuning Strategies
LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) is the recommended fine-tuning method for Z-Image Base:
1. Dataset preparation: 20-50 high-quality images minimum
2. Training parameters:
- Learning rate: 1e-4 to 5e-5
- Batch size: 1-4 (depending on VRAM)
- Steps: 1000-3000 (monitor overfitting)
3. Tools: DiffSynth-Studio, Kohya-ss trainer
Use cases:
- Product photography: Train on brand-specific product shots
- Architectural styles: Regional building aesthetics (e.g., Chinese traditional, Art Deco)
- Character consistency: Maintain specific facial features across generations
Negative Prompting Best Practices
Z-Image Base’s CFG support enables powerful negative prompting. Effective strategies:
1. Artifact suppression: “extra fingers, deformed hands, anatomical errors”
2. Style exclusion: “watercolor, sketch, painting” (when seeking photorealism)
3. Composition control: “cluttered background, centered composition, symmetrical”
4. Quality enforcement: “low resolution, jpeg artifacts, blurry”
Pro tip: Start with a comprehensive negative template, then remove elements to see their individual impact.
Bonus: Gaga AI Integration (Image-to-Video)
While Z-Image Base excels at static image generation, pairing it with Gaga AI’s video generation capabilities creates powerful multimodal workflows:
Image-to-Video Pipeline
1. Generate base image with Z-Image Base (high diversity, specific composition)
2. Feed to Gaga AI for video generation with motion control
3. Add audio fusion using Gaga AI’s audio-visual synchronization
Example workflow:
Z-Image Base → Portrait (1024×1024)
↓
Gaga AI → 5-second video (subtle smile, blink animation)
↓
Audio fusion → Add ambient music sync
This combination is particularly effective for:
- Marketing content: Product reveals with motion
- Social media: Avatar animations from static portraits
- Creative projects: Bringing concept art to life
FAQ: Z-Image Base
What is the difference between Z-Image Base and Z-Image Turbo?
Z-Image Base is the non-distilled foundation model requiring 28-50 steps and supporting CFG/negative prompts, optimized for fine-tuning. Z-Image Turbo is a distilled version requiring only 8 steps with RL enhancement, optimized for production speed and visual quality.
How do I convert Z-Image Base to GGUF format?
Use tools like llama.cpp conversion scripts or community tools from stable-diffusion.cpp. The process involves quantizing the BF16 model to Q4, Q5, or Q8 precision levels.
Does Z-Image Base support ControlNet?
Yes. As a non-distilled foundation model, Z-Image Base is fully compatible with structural conditioning methods including ControlNet, depth maps, and pose guidance. Community implementations are actively being developed.
How does Z-Image Base compare to FLUX.1-dev?
Both are foundation models designed for fine-tuning. Z-Image Base offers stronger bilingual support and is optimized for Asian aesthetics, while FLUX.1-dev has broader Western community adoption and tool support. Both use similar VAE architectures.
What is the best CFG scale for photorealism?
For photorealistic outputs, use CFG 3.5-4.5 with cfg_normalization=True. Higher values (5.0-7.0) increase prompt adherence but may reduce naturalness.
Will Z-Image-Edit be released as open source?
According to the official roadmap, Z-Image-Edit is marked “to be released” on both Hugging Face and ModelScope. The community is actively requesting its release in GitHub discussions.
Final Words
Z-Image Base represents the foundation of open-source AI image generation—prioritizing flexibility, fine-tunability, and community development over raw speed. While Z-Image Turbo serves production needs, the Base model unlocks creative possibilities for researchers, developers, and studios building custom visual AI solutions.
