Key Takeaways
- VideoMaMa is a mask-guided video matting framework that transforms coarse segmentation masks into high-quality alpha mattes using generative AI priors
- Developed by Adobe Research, Korea University, and KAIST, the model leverages Stable Video Diffusion for zero-shot generalization to real-world footage
- The framework includes the MA-V dataset containing 50,541+ real-world videos—nearly 50× larger than previous video matting datasets
- VideoMaMa’s inference code and model weights are fully open-source on GitHub and Hugging Face
- Best use cases include background replacement, visual effects compositing, and professional video editing workflows
Table of Contents
What Is VideoMaMa?
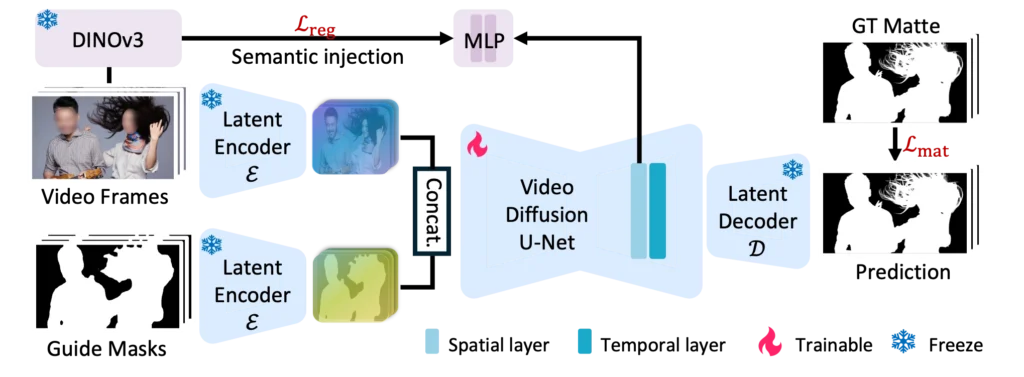
VideoMaMa (Video Mask-to-Matte Model) is an AI framework that converts rough video segmentation masks into pixel-accurate alpha mattes. The model uses pretrained video diffusion models to achieve fine-grained matting quality across diverse video domains without requiring domain-specific training.
Unlike traditional video matting approaches that struggle with synthetic-to-real generalization, VideoMaMa demonstrates strong zero-shot performance on real-world footage—even when trained exclusively on synthetic data.
Core Technical Specifications
| Feature | Specification |
| Architecture | Latent Diffusion Model (based on Stable Video Diffusion) |
| Inference Mode | Single-step diffusion |
| Training Strategy | Two-stage (spatial then temporal layers) |
| Semantic Guidance | DINOv3 feature injection |
| Input Requirements | RGB video frames + guide masks (SAM2/SAM3 output or manual) |
| Output | High-fidelity alpha matte latent variables |
How Does VideoMaMa Work?
VideoMaMa operates through a sophisticated pipeline that transforms coarse masks into refined alpha mattes. The process relies on three interconnected components.

Step 1: Input Processing
The model accepts two inputs simultaneously:
1. RGB video frames — Provides appearance details, textures, and context
2. Guide masks — Can be SAM2-generated segmentation results, manually drawn shapes, or even crude polygon approximations
Step 2: Single-Step Diffusion Inference
Unlike traditional generative models requiring dozens of iterative refinement steps, VideoMaMa uses a single forward pass to predict clean alpha latent variables. This approach delivers substantial speed improvements while maintaining output quality.
Step 3: Two-Stage Training Architecture
The training process splits into distinct phases:
1. Stage 1 (Spatial Training) — Freezes temporal layers; trains spatial layers at 1024×1024 resolution to capture fine details like hair strands and semi-transparent edges
2. Stage 2 (Temporal Training) — Freezes spatial layers; trains temporal layers on video sequences to ensure frame-to-frame consistency without flickering
Semantic Enhancement via DINOv3
VideoMaMa integrates DINOv3 features through alignment loss calculations. This addition provides stronger semantic understanding of object boundaries, addressing a common weakness where diffusion models might misidentify target objects.
What Is the MA-V Dataset?
The Matting Anything in Video (MA-V) dataset is a companion resource created using VideoMaMa’s pseudo-labeling capabilities. It addresses the critical data scarcity problem that has historically limited video matting research.

MA-V Dataset Statistics
| Metric | MA-V | Previous Largest Real-Video Dataset |
| Total Videos | 50,541 | ~1,000 |
| Content Diversity | All object categories | Primarily human subjects |
| Capture Environment | Natural settings | Controlled studio conditions |
| Annotation Quality | Semi-transparent details preserved | Hard-edge masks |
The dataset was generated by processing the SA-V dataset (SAM2’s training corpus) through VideoMaMa, converting binary segmentation masks into nuanced alpha mattes that capture motion blur, transparency, and soft edges.
How to Use VideoMaMa: Step-by-Step Guide
Prerequisites
- NVIDIA GPU with CUDA support
- Conda package manager
- Python 3.8+
- Stable Video Diffusion weights
Installation
| # Clone the repositorygit clone https://github.com/cvlab-kaist/VideoMaMa.gitcd VideoMaMa # Set up the environment (downloads dependencies automatically)# This installs Stable Video Diffusion weights and configures the virtual environmentconda activate videomama # Download model checkpoint from Hugging Face# Available at: SammyLim/VideoMaMa |
Running Inference
| python inference_onestep_folder.py \ –base_model_path “<stabilityai/stable-video-diffusion-img2vid-xt_path>” \ –unet_checkpoint_path “<videomama_checkpoint_path>” |
Input Preparation Tips
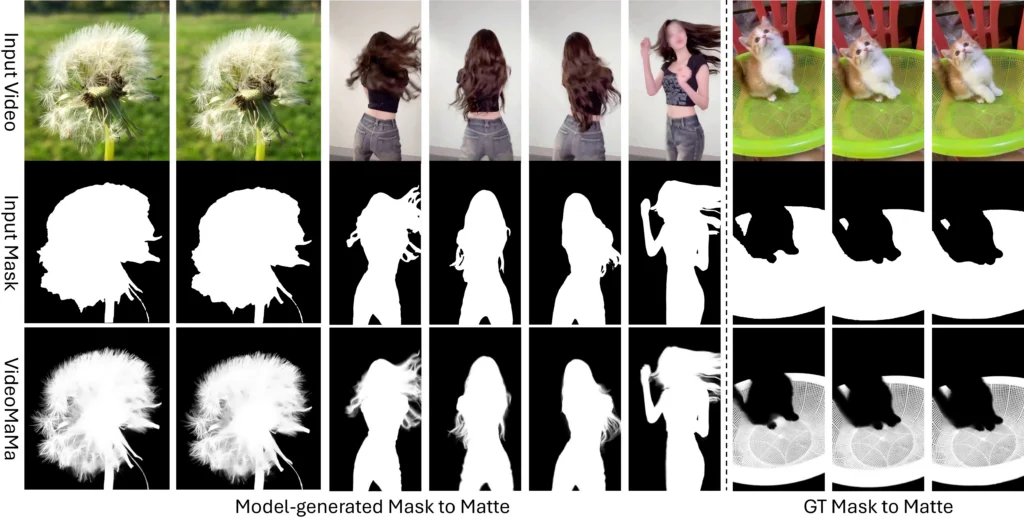
- Guide masks work best when generated by SAM2 with point or box prompts on the first frame
- The model tolerates significant mask degradation—even heavily downsampled or polygonized masks produce quality results
- For best results, ensure RGB frames are properly aligned with corresponding masks
VideoMaMa Workflow Demo: https://huggingface.co/spaces/SammyLim/VideoMaMa
VideoMaMa vs. Other Video Matting Methods
Performance Comparison
| Method | MAD (↓) | Gradient Error (↓) | Mask Tolerance | Real-World Generalization |
| VideoMaMa | Best | Best | High | Strong |
| MatAnyone | Good | Good | Medium | Moderate |
| MaGGIe | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Limited |
| MGM (Image-based) | Limited | Limited | Low | Poor |
VideoMaMa consistently outperforms alternatives across benchmark tests including V-HIM60 and YouTubeMatte, particularly when handling degraded input masks or model-generated segmentation results.
SAM2-Matte: The Downstream Application
When SAM2 is fine-tuned on the MA-V dataset, the resulting SAM2-Matte model achieves state-of-the-art performance on first-frame guided video matting tasks. On the YouTubeMatte 1920×1080 benchmark, SAM2-Matte reaches a MAD score of 1.2695—significantly better than dedicated matting methods like MatAnyone.
What Are the Limitations of VideoMaMa?
VideoMaMa represents a significant advancement, but certain constraints remain:
1. Initial Mask Dependency — If the input mask completely misidentifies the target object, VideoMaMa cannot self-correct; upstream segmentation accuracy (from SAM2/SAM3) remains important
2. Computational Requirements — The Stable Video Diffusion backbone demands substantial GPU resources
3. Training Code Status — As of January 2025, training code remains under internal review at the research institutions
Practical Applications for VideoMaMa
Professional Video Editing
Extract subjects from complex backgrounds without green screens, handling natural footage with semi-transparent elements like hair, smoke, or motion blur.
Visual Effects Compositing
Generate production-quality alpha channels for layered compositions, enabling seamless integration of live-action footage with CGI elements.
Background Replacement
Remove or substitute backgrounds in recorded video content while preserving fine edge details that traditional keying methods miss.
Content Creation Workflows
Automate extraction of subjects for social media content, educational videos, or marketing materials at scale.
Bonus: Enhance Your Video Workflow with Gaga AI
While VideoMaMa handles the technical challenge of extracting subjects from video, you’ll need compelling content to work with. Gaga AI offers a complementary solution for creating the video footage itself.
What Is Gaga AI?
Gaga AI is a next-generation autoregressive AI video generator powered by the GAGA-1 video model. It animates static portraits into lifelike AI avatars with precise lip-sync, producing cinematic videos that feel coherent and alive.
Why Gaga AI Stands Out
At its core, GAGA-1 uses a co-generation architecture. Instead of creating voice, lip sync, and expressions in isolation, it generates them together in real time. The voice is not added later—it’s born within the model’s generation process.
This eliminates common AI video problems:
- Disjointed lip synchronization
- Flat, emotionless facial animations
- The uncanny valley effect
- Fragmented workflows requiring multiple tools
Gaga AI Capabilities
| Feature | Specification |
| Input Format | JPEG, PNG, JPG (max 10MB) |
| Audio Support | MP3, WAV, OGG, AAC, M4A (max 20MB) |
| Output Quality | 720p resolution |
| Generation Speed | 10-second video in 3-4 minutes |
| Access | Free, no paywall |
How Gaga AI Complements VideoMaMa
A practical workflow combining both tools:
1. Generate character footage with Gaga AI using a portrait image and script
2. Create segmentation masks using SAM2/SAM3
3. Refine masks to alpha mattes with VideoMaMa
4. Composite the extracted subject onto new backgrounds or VFX elements
This pipeline enables creating professional-quality visual content from a single photograph—no actors, studios, or green screens required.
Getting Started with Gaga AI
1. Visit gaga.art
2. Upload a portrait image (1080×1920 for vertical, 1920×1080 for horizontal)
3. Add your script or audio file
4. Generate and download your video
Frequently Asked Questions
Is VideoMaMa free to use?
Yes. VideoMaMa’s inference code and model weights are open-source under the Stability AI Community License. The checkpoint is available on Hugging Face at SammyLim/VideoMaMa.
What hardware do I need to run VideoMaMa?
VideoMaMa requires an NVIDIA GPU with CUDA support. The model is built on Stable Video Diffusion, so hardware capable of running SVD will support VideoMaMa inference.
Can VideoMaMa work without SAM2?
Yes. While SAM2-generated masks provide convenient input, VideoMaMa accepts any binary or soft mask input—including manually drawn masks or outputs from other segmentation tools.
How does VideoMaMa handle motion blur?
VideoMaMa excels at capturing motion blur in alpha mattes. The model learns natural motion patterns from its video diffusion prior, enabling accurate transparency estimation even for fast-moving subjects.
What’s the difference between VideoMaMa and MatAnyone?
VideoMaMa uses generative priors from video diffusion models and focuses on mask-to-matte conversion. MatAnyone uses memory propagation for temporal consistency. VideoMaMa demonstrates stronger generalization to diverse real-world footage and better tolerance for degraded input masks.
Is the MA-V dataset publicly available?
The MA-V dataset release status should be verified on the official project page (cvlab-kaist.github.io/VideoMaMa), as data releases may follow different timelines than code releases.
Can I train my own VideoMaMa model?
Training code is currently under internal review at the research institutions. Monitor the GitHub repository for release announcements.
What video formats does VideoMaMa support?
VideoMaMa processes video as frame sequences. Standard image formats (PNG, JPEG) for frames are supported. The inference script handles folder-based input containing sequential frames.